Harmonic Centrality
The Harmonic Centrality algorithm calculates the harmonic centrality of each vertex in the graph. Harmonic Centrality is a variant of Closeness Centrality. In a (not necessarily connected) graph, the harmonic centrality reverses the sum and reciprocal operations in the definition of closeness centrality:
For more information, see Harmonic Centrality.
Specifications
CREATE QUERY harmonic_cent(SET<STRING> v_type, SET<STRING> e_type,
SET<STRING> re_type,INT max_hops=10, INT top_k=100, BOOL wf = TRUE,BOOL print_accum = True, STRING result_attr = "", STRING file_path = "", BOOL display_edges = FALSE)Parameters
| Name | Description | Data type |
|---|---|---|
|
Vertex types to calculate harmonic centrality for |
|
|
Edge types to traverse |
|
|
Reverse edge types |
|
|
The maximum number of hops the algorithm would consider for each vertex. If set to a non-positive value, the limit is ignored. |
|
|
Sort the scores high to low and output the highest |
|
|
If |
|
|
If |
|
|
If not empty, store centrality values (FLOAT) to this attribute |
|
|
If not empty, write output to this file in CSV. |
|
|
If |
|
Example
If we have the following graph, we can see that Ivy is the most central of the five vertices. Running the algorithm on the graph shows that Ivy has the highest centrality score:
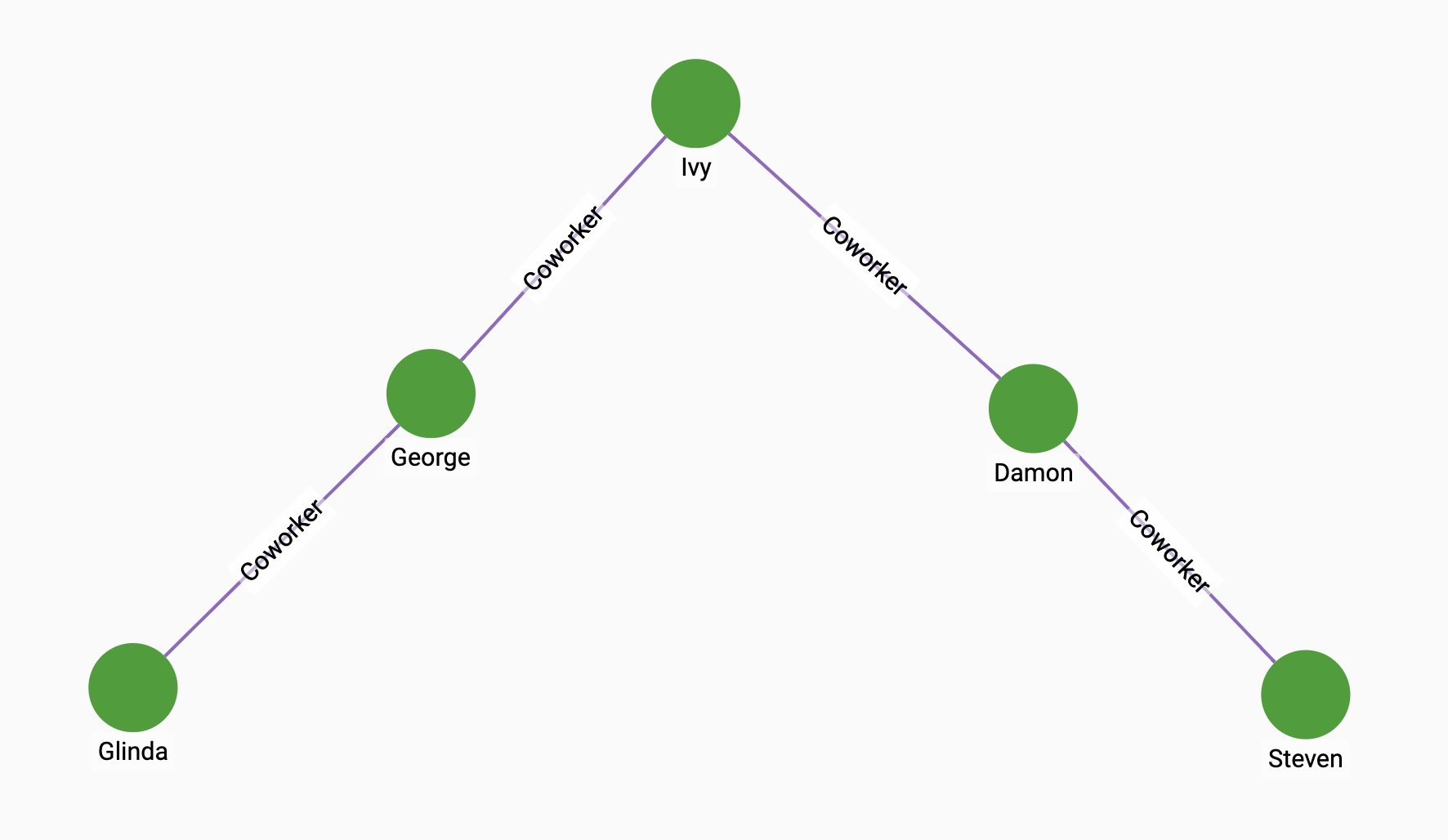
RUN QUERY harmonic_cent(["Person"], ["Coworker"], ["Coworker"], 4, 5,
true, true, _, _, _){
"error": false,
"message": "",
"version": {
"schema": 0,
"edition": "enterprise",
"api": "v2"
},
"results": [{"top_scores": [
{
"score": 0.04167,
"Vertex_ID": "Ivy"
},
{
"score": 0.03571,
"Vertex_ID": "Damon"
},
{
"score": 0.03571,
"Vertex_ID": "George"
},
{
"score": 0.025,
"Vertex_ID": "Steven"
},
{
"score": 0.025,
"Vertex_ID": "Glinda"
}
]}]
}